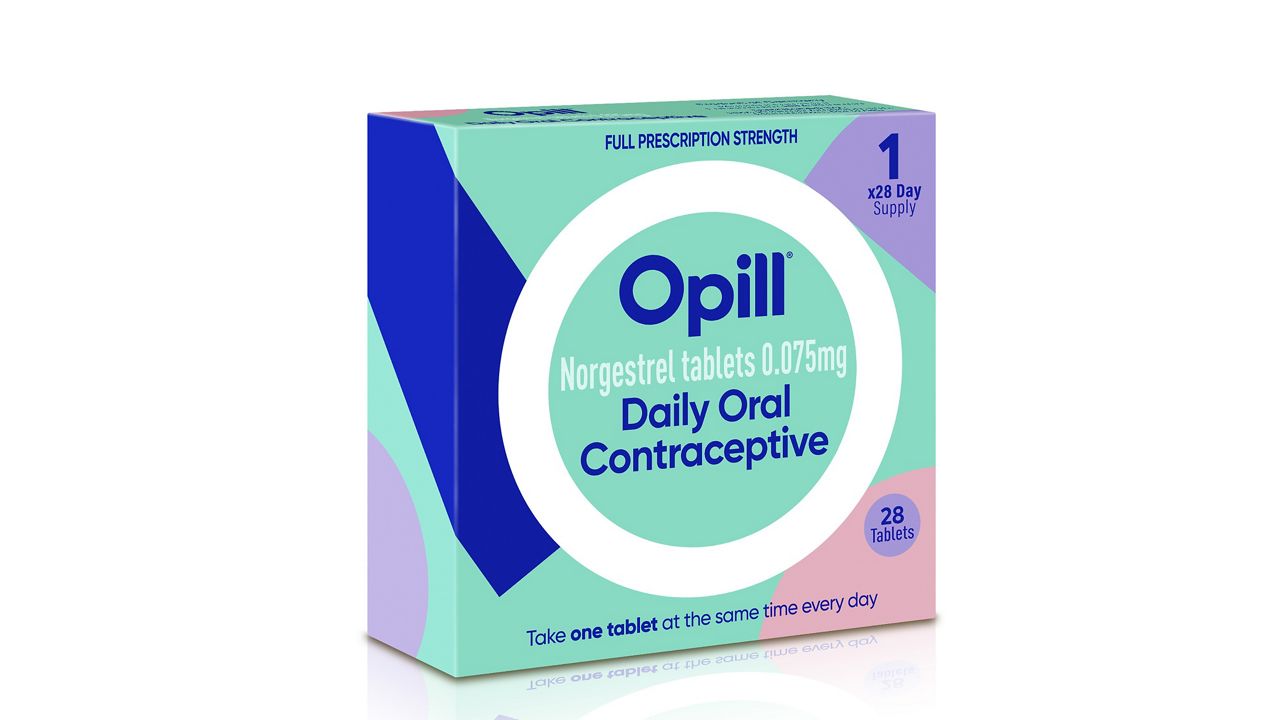
MADISON, Wis. (AP) — Medicaid recipients in Wisconsin will have access to the first over-the-counter birth control pill starting Tuesday, allowing them to receive contraceptive medication with no out-of-pocket costs or doctor's prescription, Gov. Tony Evers announced.
Evers, a Democrat, promised in his State of the State speech in January that Opill would be available to people in the state's Medicaid program known as BadgerCare Plus. It will start becoming available in some Medicaid-enrolled pharmacies on Tuesday and expand over the coming weeks, Evers said in a statement.
Evers said it was more important than ever to ensure access to the drug “as we see continued attacks on women’s reproductive freedoms here in Wisconsin and across our country.”
BadgerCare Plus currently covers over-the-counter daily oral contraception with a prescription from a provider. A new standing order from Evers will allow for Opill to be available without a prescription and with no out-of-pocket costs.
The suggested retail price from manufacturer Perrigo for a one-month supply is about $20.
The Food and Drug Administration in July approved the sale of once-a-day Opill without a prescription.
The availability of the pill to women nationwide, not just those on Medicaid, gives them another birth control option amid the legal and political battles over reproductive health, including the Supreme Court's 2022 decision that overturned Roe v. Wade. That ruling upended abortion access across the U.S.
Hormone-based pills have long been the most common form of birth control in the U.S., used by tens of millions of women since the 1960s. Until Opill's approval, all required a prescription.
Opill is an older class of contraceptives, sometimes called minipills, that contain a single synthetic hormone, progestin. Minipills generally carry fewer side effects than more popular combination estrogen and progestin pills.